RED: Requirements EDitor
Our main tool is RED, a classic stand-alone desktop application that serves as a Requirements Engineer's workstation. It aspires to complete and coherent in concepts and notations, and offers advanced features straight from the lab that are not usually found in commercial tools. In that sense, RED is also a work bench for RE researchers that want to implement their latest ideas in a realisitc setting so that they would become validatable on large case studies.
RED is implemented in JAVA, and is built on the Eclipse Rich Client Platform, using, among others AgileGrid, JFaces, EMF, and GEF2.
RED is available as open source software under the Apache 2.0 license.
Concepts
As we have said before, the most important yet least prominent feature of the RED tool is its alignment with the accompanying lecture material of DTU course 02264. Both present the same material and thus offer alternative approaches to learning. The alignment is implemented as a coherent and comprehensive meta-model underlying RED. And what the user sees on the UI is exactly what the model contains.
More specifically, RED provides a comprehensive set of specification concepts, as illustrated by the following figure.
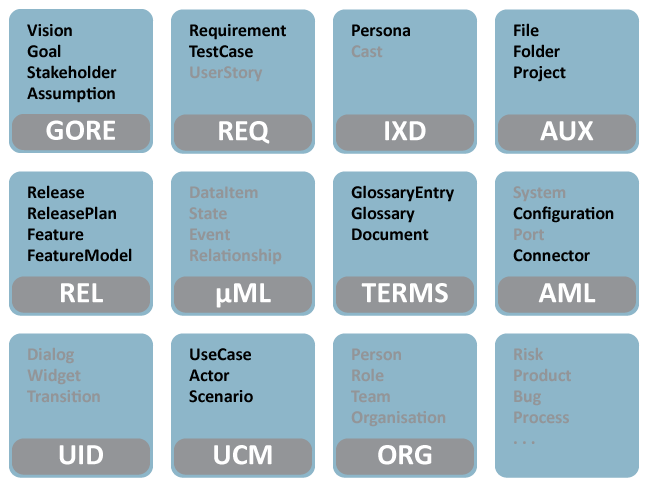
Fig. 1 - RED Specifcation Concepts (concepts under development are greyed out).

Classic Textual Requirements
The single most widely used way of specifying requirements is by prose. RED supports rich prose descriptions with all necessary management, cost/benefit, and tracing attributes.
Technical Terminology
RED also supports conventional glossaries of technical terminology. Glossaries allow definitions in terms of cross-referencing descriptions, synonymy, antonyms, aggregation and taxonomic hierarchies. The next version of this plugin will allow multiple language
Goal Oriented Requirements Engineering
The very basic concepts of GORE are provided, including visions and assumptions, and of course goals and stakeholders. Most other GORE concepts overlap heavily with other approaches to specification and modeling and are covered there.
Release Planning
Based on other concepts like use cases and systems, requirement engineers can create release plans to interactively balance cost and delivery dates. Release plans may be visualized.
Architectural Modeling
Architecture is the dual twin of RE, and many software architectural concepts are also classic RE concepts, such as system context and actors. The AM plugin provides also connectors and configurations to complete the conceptual coverage. Behavioral details are covered in the forthcoming software modeling plugin.
Auxialiary Concepts
For housekeeping, there are also representations of projects, files, and folders, and external documents that may be integrated into a RED project.
Interaction Design
An effecitve way of specifying UI-heavy systems is by iteratively sketching out the user interface and validating it. Typical concepts used in this approach are personas, scenarios, and casts. Scenarios appear also in other contexts, such as use case modelign and are covered there.
Use Case Modeling
Use Cases are one of the most popular ways of specifying features. They are half way between classic textual requirements and more specific modeling, e.g., UML-type specifications.
Software Modeling
Software modeling a la UML is important not just for the more technical later stages, but also to enrich architectural and use case modeling to become more useful. It comprises notions of state, event, data, and association. This plugin is expected in Q3/2016.
Features
All of the specification concepts explained above have a forms-based editor with extensive management and tracing support. Many of them also provide visual editors.Beyond that, RED offers a number of practical tools for requirements specification.

Fig. 2 - RED Specifcation Tools (tools under development are greyed out).

Tracing
A simple yet powerful tracing interface allows bidirectional tracing of any elements according to a multitude of dimensions. Visual tracing is presently missing.
Stitching
Overlapping diagrams representing model fragments may be stitched together to validate the (sets of) requirements that are illustrated by the fragments and to support the transitoin from analysis to design.
Aggregation
Quantitative aspects like cost, benefit, risk, latency, duration and so on may be aggregated over sets of elements so as to allow informed decisions i npriorituzatio nand planing.
Estimation
Cost and benefit estimation are important sources of inforamtion for management decisions. Beyond manual estimation methods, RED also offers to apply the Use Case Point method in order to automatically derive estimates from sufficiently detailed specifications.
Reporting
Requirements specifications may be compiled into reports that are suitable for sharing online as HTML, or for being included as appendices to contractual documents.
Merging
In order to accommodate for conflicting versions arising from concurrent projects, RED allows to split specification across multiple files, and provides a merge feature to mitigate conflicts interactively.
Enactment
Scenarios may be enacted and converted to speech output in order to facilitate validation of scenarios. Complex operators lke loop, call, exception, and parallel execution allow arbitrary scenarios. Scenarios may be textual or visual in nature.
Inspection Support
Special facilities are added to support spcification inspections. In particular, parts of a specification may be password-protected against accidental changes.
Visual Modeling
Many specification concepts allow a natural visualisation, and visual modeling. Specification and visual elements are both treated as first class citizens: they can be specified separately or together, where the connection between them can be established and severed at any time.
Planguage Identifiers
The user can identify elements by proper names that may be rather long and descriptive. For practical purposes, he can also provide a short label, suich as an abbreviation, acronym, or "nick name". RED automatically aggregates these (and the element type) into Planguage-style composite names.



